近日,我校农业微生物资源发掘与利用全国重点实验室、动物育种与健康养殖前沿科学中心、湖北洪山实验室、动科动医学院孙铝辉教授课题组在《Science Advances》期刊上发表了题为“Loss of SELENOW aggravates muscle loss with regulation of protein synthesis and ubiquitin-proteasome system”的研究论文。该研究首次揭示了硒蛋白W(SELENOW)在肌肉萎缩中的重要功能及机制。

硒是人和动物所必需的微量元素,主要以25个硒蛋白的形式发挥生物学功能。然而,我国有超过2/3以上的国土面积存在硒的缺乏,导致人和动物均面临着营养性缺硒的风险。在集约化的畜禽养殖业中,高密度饲养、热应激、有害气体及霉菌毒素等多种应激源常使动物处于亚健康状态,使得畜禽对硒的需要量升高,严重情况下,甚至诱发群体性营养性缺硒疾病的发生,如缺硒性肌营养不良症(NMD),它会引起动物生长发育的迟缓和肉品质下降,给养殖业造成巨大经济损失。
课题组前期研究发现,缺硒诱导肉鸡NMD发生与肌肉中一碳代谢紊乱诱导机体免疫系统和氧化还原稳态失衡相关,其中,SELENOW在此过程中下调尤为显著(JournalofNutrition,2023)。然而,SELENOW在NMD发生中的作用与机制尚不清楚。因此,本研究系统性探究了SELENOW在肌肉中的功能。研究结果表明,正常生理条件下,SELENOW的缺失并不影响动物的生长和肌肉的发育;在地塞米松诱导的急性肌肉萎缩和自然衰老相关的慢性肌肉萎缩条件下,SELENOW会表达上调,然而,SELENOW的缺失会加剧此萎缩条件下肌肉质量的流失;体内外过表达SELENOW,可缓解地塞米松诱导的肌管和肌肉萎缩。
进一步的机制研究表明,SELENOW通过与RAC1蛋白互作,调控RAC1-mTOR级联信号通路。当SELENOW缺失时,通过抑制RAC1-mTOR级联导致肌肉内蛋白质合成减少,泛素化降解加速,从而加剧了肌肉萎缩的进程。
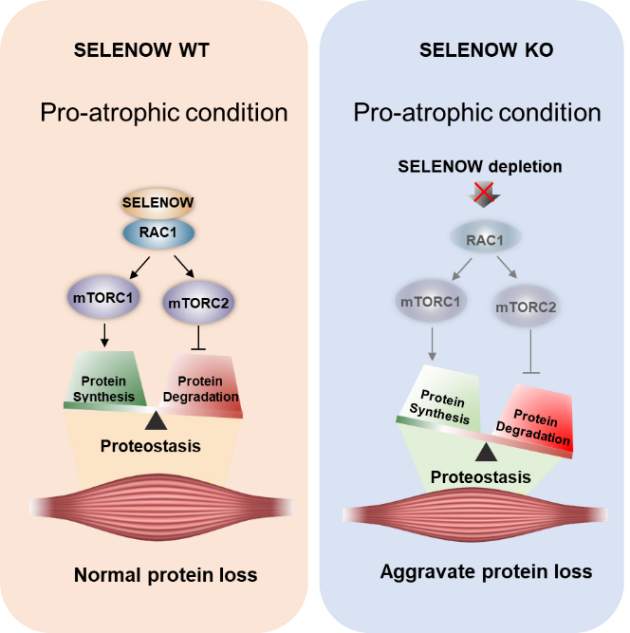
图1 SELENOW通过调控RAC1-mTOR级联参与蛋白质稳态调节
本研究揭示了SELENOW缺失通过抑制RAC1-mTOR级联加剧肌肉萎缩。研究结果为合理应用硒防控畜禽NMD提供了新的科学依据,也为预防和治疗人类肌肉萎缩提供了潜在的靶点。
华中农业大学动科动医学院已毕业博士杨嘉成(现为动科动医学院博士后)为论文第一作者,孙铝辉教授为论文的通讯作者。美国康奈尔大学雷新根教授、湖北省农业科学院魏金涛副研究员等也参与了本项研究。该研究得到科技创新2030-重大项目、青年拔尖人才支持计划、国家自然科学基金和中央高校基础研究基金的支持。
【英文摘要】
Sarcopenia is characterized by accelerated muscle mass and function loss, which burdens and challenges public health worldwide. Several studies indicated that selenium deficiency is associated with sarcopenia; however, the specific mechanism remains unclear. Here, we demonstrated that selenoprotein W (SELENOW) containing selenium in the form of selenocysteine functioned in sarcopenia. SELENOW expression is up-regulated in dexamethasone (DEX)–induced muscle atrophy and age-related sarcopenia mouse models. Knockout (KO) of SELENOW profoundly aggravated the process of muscle mass loss in the two mouse models. Mechanistically, SELENOW KO suppressed the RAC1-mTOR cascade by the interaction between SELENOW and RAC1 and induced the imbalance of protein synthesis and degradation. Consistently, overexpression of SELENOWin vivoandin vitroalleviated the muscle and myotube atrophy induced by DEX. SELENOW functioned in age-related sarcopenia and regulated the genes associated with aging. Together, our study uncovered the function of SELENOW in age-related sarcopenia and provides promising evidence for the prevention and treatment of sarcopenia.
【文章链接】:https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adj4122